How to run a command with a timeout limit in Linux?
Linux comes with many general command line tools to make our work easy and efficient. We can use these tools in script and programs to be a better programmer. Today we will discuss the timeout command line utility which comes pre-installed with Linux.
How to execute Linux commands with a time limit?
timeout is a command-line tool which allows you to run a Linux command and set a time limit for it. It basically kills the command if it is still running after the DURATION specified.
Let's take a look at the syntax of timeout command:
timeout [OPTION] DURATION COMMAND [ARG]...
timeout [OPTION]
Brief description of options available with the timeout command.
| Option |
Description |
--preserve-status |
exit with the same status as COMMAND, even when the command times out
|
--foreground |
when not running timeout directly from a shell prompt, allow COMMAND to read from the TTY and get TTY signals; in this mode, children of COMMAND will not be timed out.
|
-k, --kill-after=DURATION |
also send a KILL signal if COMMAND is still running this long after the initial signal was sent.
|
-s, --signal=SIGNAL |
specify the signal to be sent on timeout; SIGNAL may be a name like 'HUP' or a number; see 'kill -l' for a list of signals
|
-v, --verbose |
diagnose to STDERR any signal sent upon timeout. |
--help |
display this help and exit. |
--version |
output version information and exit. |
How to run a command with the timeout command and specify duration?
You can use the basic syntax of timeout command to get started with timeout command.
In this example we executed the ping bing.com command for 2.9 seconds.
timeout DURATION COMMAND
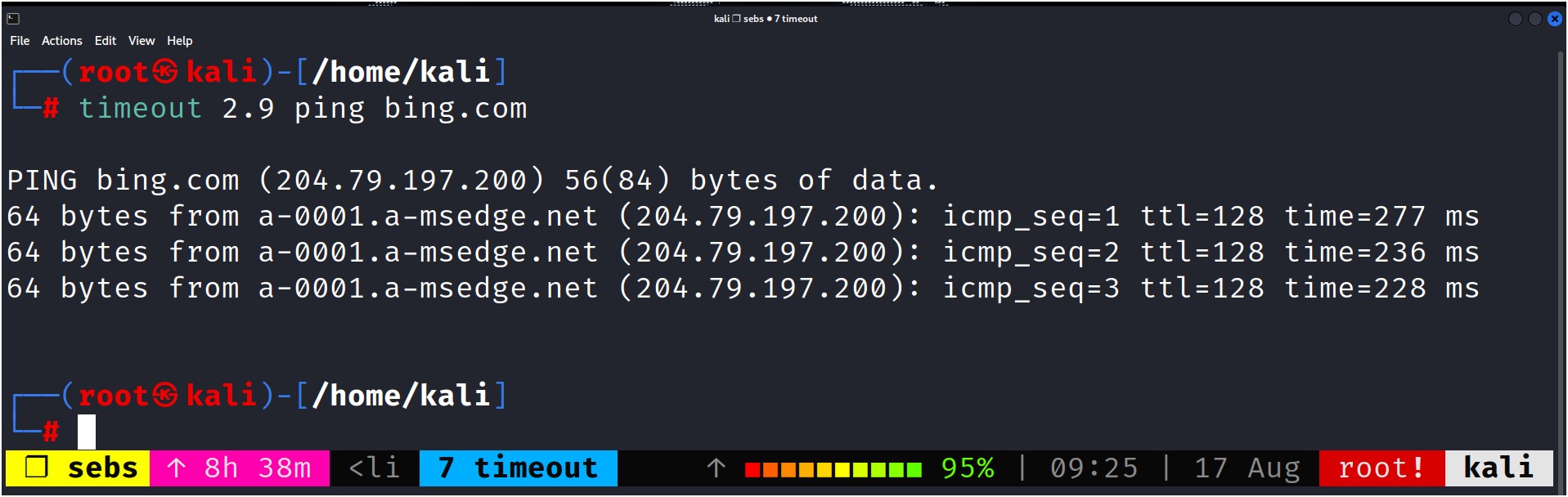
Run a command for specified DURATION with timeout for Linux.
The DURATION for timeout command can be a positive integer or a floating-point number:
s - seconds (default)m - minutesh - hoursd - days
How to preserve STATUS CODE with timeout command in Linux?
To return the exit status of the command even when the time limit is reached, use the --preserve-status option as:
timeout --preserve-status DURATION COMMAND
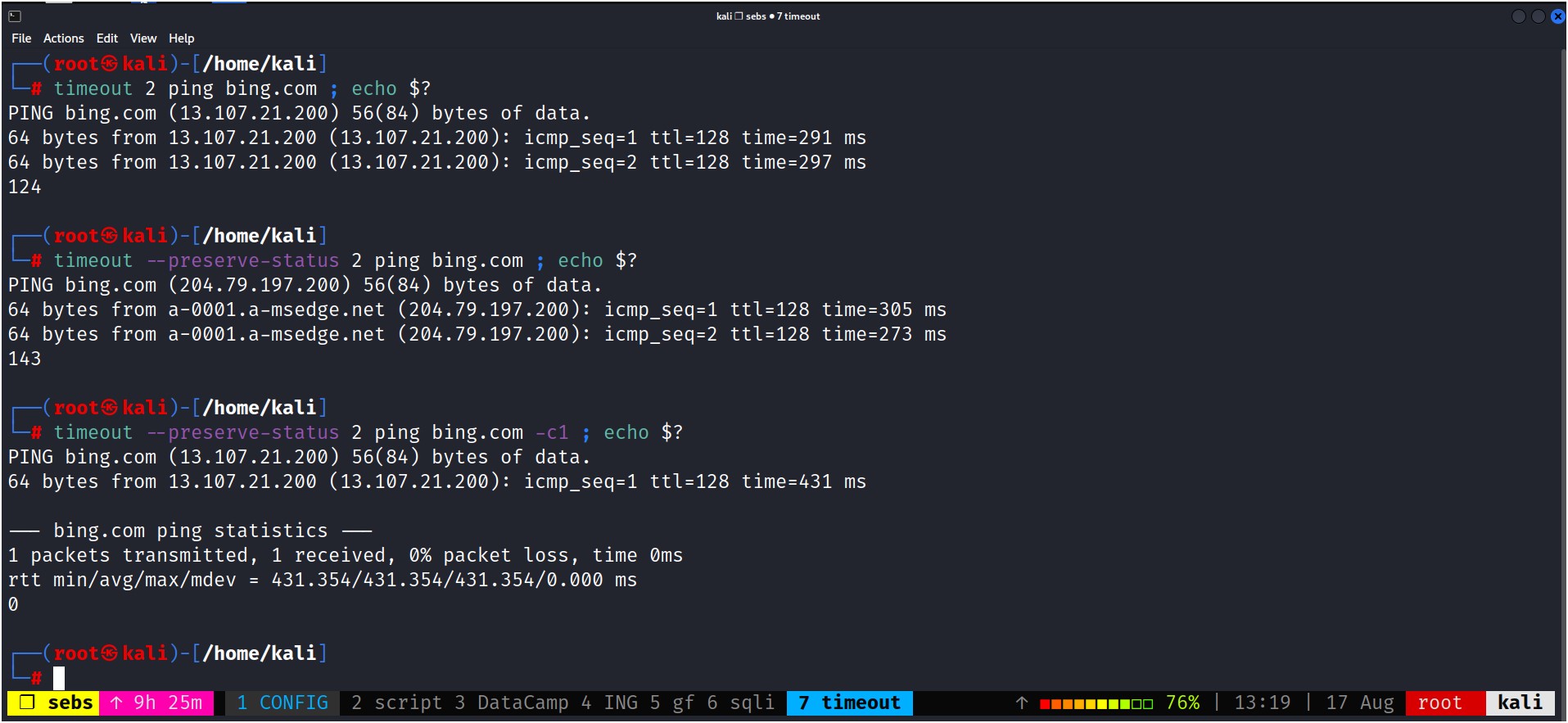
How to run command in foreground with timeout command in Linux?
To run a command or script in foreground. you can use --foreground option with timeout command.
timeout --foreground DURATION COMMAND
How to kill a command after a certain duration with timeout command in Linux?
To send a KILL signal to the command after the DURATION after the time limit with timeout command.
timeout --kill-after=DURATION DURATION COMMAND
How to send a specific SIGNAL to a command when the time limit is reached with timeout command in Linux?
timeout sends a SIGTERM signal as default when no SIGNAL is specified. There are many Linux SIGNALs available. To get a list of all available SIGNALs, use kill command with -l option.
kill -l
You can specify which signal to send using the -s (--signal) option.
timeout --signal INT 5s sleep 10
You can specify the signal by its number like 9.
timeout -s 9 5m sleep 10m
Conclusion
In this tutorial. you learned that the timeout command is used to run a given command with a time limit. It is quite a simple command to make your life easy while creating scripts and automation.