LAST UPDATED ON: SEPTEMBER 16, 2024
What is Multithreading?
In plain english, Multithreading means executing multiple threads parallely.
So let's start by understanding, what is a thread?
Thread is an execution unit that consists of its own program counter, a stack, and a set of registers where the program counter mainly keeps track of which instruction to execute next, a set of registers mainly hold its current working variables, and a stack mainly contains the history of execution
Threads are also known as Lightweight processes. Threads are a popular way to improve the performance of an application through parallelism. Threads are mainly used to represent a software approach in order to improve the performance of an operating system just by reducing the overhead thread that is mainly equivalent to a classical process.
The CPU switches rapidly back and forth among the threads giving the illusion that the threads are running in parallel.
As each thread has its own independent resource for process execution; thus Multiple processes can be executed parallelly by increasing the number of threads.
It is important to note here that each thread belongs to exactly one process and outside a process no threads exist. Each thread basically represents the flow of control separately. In the implementation of network servers and web servers threads have been successfully used. Threads provide a suitable foundation for the parallel execution of applications on shared-memory multiprocessors.
The given below figure shows the working of a single-threaded and a multithreaded process:
![What are threads]()
Before moving on further let us first understand the difference between a process and a thread.
| Process |
Thread |
| A Process simply means any program in execution. |
Thread simply means a segment of a process. |
| The process consumes more resources |
Thread consumes fewer resources. |
| The process requires more time for creation. |
Thread requires comparatively less time for creation than process. |
| The process is a heavyweight process |
Thread is known as a lightweight process |
| The process takes more time to terminate |
The thread takes less time to terminate. |
| Processes have independent data and code segments |
A thread mainly shares the data segment, code segment, files, etc. with its peer threads. |
| The process takes more time for context switching. |
The thread takes less time for context switching. |
| Communication between processes needs more time as compared to thread. |
Communication between threads needs less time as compared to processes. |
| For some reason, if a process gets blocked then the remaining processes can continue their execution |
In case if a user-level thread gets blocked, all of its peer threads also get blocked. |
Advantages of Thread
Some advantages of thread are given below:
-
Responsiveness
-
Resource sharing, hence allowing better utilization of resources.
-
Economy. Creating and managing threads becomes easier.
-
Scalability. One thread runs on one CPU. In Multithreaded processes, threads can be distributed over a series of processors to scale.
-
Context Switching is smooth. Context switching refers to the procedure followed by the CPU to change from one task to another.
-
Enhanced Throughput of the system. Let us take an example for this: suppose a process is divided into multiple threads, and the function of each thread is considered as one job, then the number of jobs completed per unit of time increases which then leads to an increase in the throughput of the system.
Types of Thread
There are two types of threads:
-
User Threads
-
Kernel Threads
User threads are above the kernel and without kernel support. These are the threads that application programmers use in their programs.
Kernel threads are supported within the kernel of the OS itself. All modern OSs support kernel-level threads, allowing the kernel to perform multiple simultaneous tasks and/or to service multiple kernel system calls simultaneously.
Let us now understand the basic difference between User level Threads and Kernel level threads:
| User Level threads |
Kernel Level Threads |
| These threads are implemented by users. |
These threads are implemented by Operating systems |
| These threads are not recognized by operating systems, |
These threads are recognized by operating systems, |
| In User Level threads, the Context switch requires no hardware support. |
In Kernel Level threads, hardware support is needed. |
| These threads are mainly designed as dependent threads. |
These threads are mainly designed as independent threads. |
| In User Level threads, if one user-level thread performs a blocking operation then the entire process will be blocked. |
On the other hand, if one kernel thread performs a blocking operation then another thread can continue the execution. |
| Example of User Level threads: Java thread, POSIX threads. |
Example of Kernel level threads: Window Solaris. |
| Implementation of User Level thread is done by a thread library and is easy. |
While the Implementation of the kernel-level thread is done by the operating system and is complex. |
| This thread is generic in nature and can run on any operating system. |
This is specific to the operating system. |
Multithreading Models
The user threads must be mapped to kernel threads, by one of the following strategies:
-
Many to One Model
-
One to One Model
-
Many to Many Model
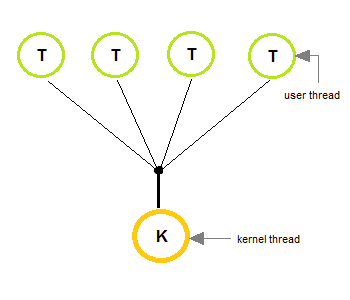
1. Many to One Model
-
In the many to one model, many user-level threads are all mapped onto a single kernel thread.
-
Thread management is handled by the thread library in user space, which is efficient in nature.
-
In this case, if user-level thread libraries are implemented in the operating system in some way that the system does not support them, then the Kernel threads use this many-to-one relationship model.
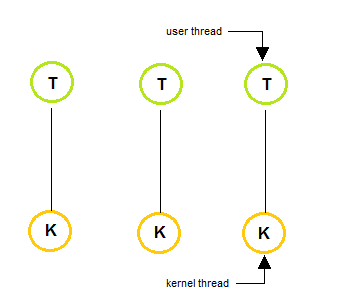
2. One to One Model
-
The one to one model creates a separate kernel thread to handle each and every user thread.
-
Most implementations of this model place a limit on how many threads can be created.
-
Linux and Windows from 95 to XP implement the one-to-one model for threads.
-
This model provides more concurrency than that of many to one Model.
3. Many to Many Model
-
The many to many model multiplexes any number of user threads onto an equal or smaller number of kernel threads, combining the best features of the one-to-one and many-to-one models.
-
Users can create any number of threads.
-
Blocking the kernel system calls does not block the entire process.
-
Processes can be split across multiple processors.

What are Thread Libraries?
Thread libraries provide programmers with API for the creation and management of threads.
Thread libraries may be implemented either in user space or in kernel space. The user space involves API functions implemented solely within the user space, with no kernel support. The kernel space involves system calls and requires a kernel with thread library support.
Three types of Thread
-
POSIX Pitheads may be provided as either a user or kernel library, as an extension to the POSIX standard.
-
Win32 threads are provided as a kernel-level library on Windows systems.
-
Java threads: Since Java generally runs on a Java Virtual Machine, the implementation of threads is based upon whatever OS and hardware the JVM is running on, i.e. either Pitheads or Win32 threads depending on the system.
Multithreading Issues
Below we have mentioned a few issues related to multithreading. Well, it's an old saying, All good things, come at a price.
1. Thread Cancellation
Thread cancellation means terminating a thread before it has finished working. There can be two approaches for this, one is Asynchronous cancellation, which terminates the target thread immediately. The other is Deferred cancellation allows the target thread to periodically check if it should be canceled.
2. Signal Handling
Signals are used in UNIX systems to notify a process that a particular event has occurred. Now in when a Multithreaded process receives a signal, to which thread it must be delivered? It can be delivered to all or a single thread.
3. fork() System Call
fork() is a system call executed in the kernel through which a process creates a copy of itself. Now the problem in the Multithreaded process is, if one thread forks, will the entire process be copied or not?
4. Security Issues
Yes, there can be security issues because of the extensive sharing of resources between multiple threads.
There are many other issues that you might face in a multithreaded process, but there are appropriate solutions available for them. Pointing out some issues here was just to study both sides of the coin.